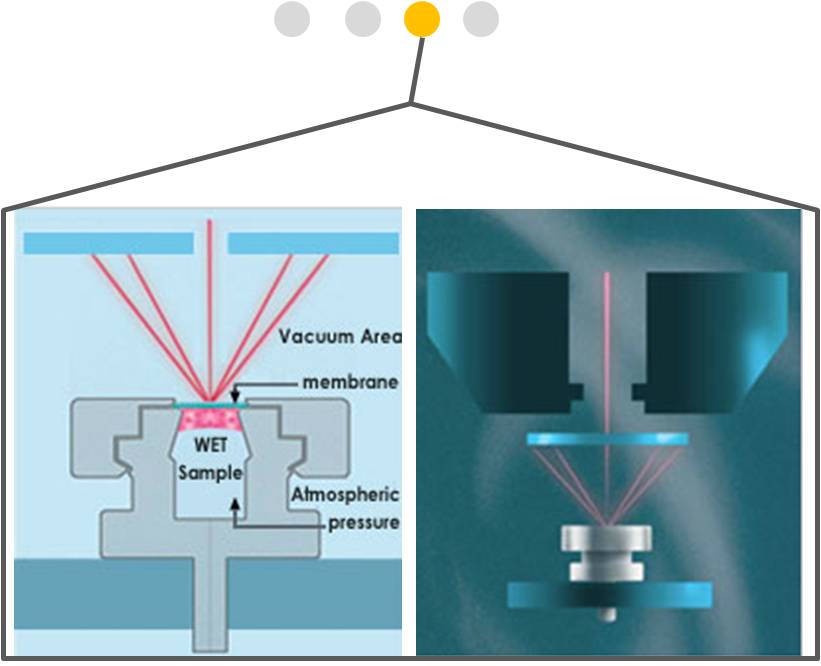


一、 SEM液态样品套件SP-102-24
WET SEM是一个应用于SEM样品台的含水样品室。在样品室的中心区域覆盖一层纳米薄膜,完全将含水样品与电镜真空室隔离,电子束穿透薄膜成像。
SP-102-24套件适用于扫描液态及溶液中颗粒样品,包含QX-102样品室及所有必需配件。
1. QX-102 Capsules (24 units) »
2. MP-10 Multi-well Plates (2 units) »
4. RT-56 Calibration Capsule »
5. AT-60 Aspirator Tips (60 units) »
6. User Manual, Applications Manual, Instructional Training Movie, WETSEMTM Imaging Quick Guide
QX-102样品室

QX-102样品室适用于多种含水丰富的材料和生物样品,比如食物、化妆品、油、墨水、溶液中的颗粒、附着或非附着细胞、微生物等。使用QX-012样品室,很容易观察不同粘稠度的样品如泡沫状、凝胶状、奶油状、乳胶状。样品既可以直接观察,也可以做适当的染色增强对比或标记处理。该样品室就像一个细胞培养皿,特别为SEM设计。样品不需要包埋及嵌入处理。相对于光学显微镜,现在电镜成像的样品处理更加简单。
MP-10 Multi多孔板

多孔板用于同时处理多个QX-102样品室。不同操作同时进行,如:细胞培养,在倒置光学显微镜观察。在样品处理过程中保持其湿度,并能与实验室标准仪器兼容。多孔板经无菌处理,一盒2个。
IB-64 Imaging Buffer
QX Imaging Buffer适用于QX-102样品舱在SEM扫描前处理样品,能降低电子束对样品的损伤。经无菌处理,冷冻保存。
RT-56标准样品

标准样品帮助第一次使用WETSEM的用户找到扫描电镜成像时的合适参数。标准样品包含40nm和500nm两种不同大小的纳米颗粒。纳米颗粒很容易在电镜中观察到,帮助确定适合的参数。
AT-60 吸管枪头

吸管枪头可安全方便的从单个QX-102样品舱中吸取液体样品。枪头适用于任何标准的移液器。如使用多个试剂盒或多个液体样品,推荐使用MA-4多孔吸管,可以同时提取多个液体样品。灭菌的吸管枪头一盒60个。

二、 SEM动态水合作用套件SK-102-24
SK-102-24 应用于细胞生物和液体样品
包含QX-102样品室及所有必需配件:
1. QX-102 Capsules (24 units)
2. MP-10 Multi-well Plates (2 units)
3. MA-4 Multi-well Aspirator
4. IB-64 Imaging Buffer
5. RT-56 Calibration Capsule
6. User Manual, Applications Manual, Instructional Training Movie, WETSEMTM Imaging Quick Guide
QX-102样品室

QX-102样品室适用于多种含水丰富的材料和生物样品,比如食物、化妆品、油、墨水、溶液中的颗粒、附着或非附着细胞、微生物等。使用QX-012样品室,很容易观察不同粘稠度的样品如泡沫状、凝胶状、奶油状、乳胶状。样品既可以直接观察,也可以做适当的染色增强对比或标记处理。该样品室就像一个细胞培养皿,特别为SEM设计。样品不需要包埋及嵌入处理。相对于光学显微镜,现在电镜成像的样品处理更加简单。
MP-10 Multi多孔板

多孔板用于同时处理多个QX-102样品室。不同操作同时进行,如:细胞培养,在倒置光学显微镜观察。在样品处理过程中保持其湿度,并能与实验室标准仪器兼容。多孔板经无菌处理,一盒2个。
MA-4 Multi-well Aspirator

多吸管用于QX-102密封室吸取液体,一次可以同时在MP-10多孔板上对4个密封室抽取液体。多吸管能连接任何标准的真空泵。
IB-64 Imaging Buffer
QX Imaging Buffer适用于QX-102样品舱在SEM扫描前处理样品,能降低电子束对样品的损伤。经无菌处理,冷冻保存。
RT-56标准样品

标准样品帮助第一次使用WETSEM的用户找到扫描电镜成像时的合适参数。标准样品包含40nm和500nm两种不同大小的纳米颗粒。纳米颗粒很容易在电镜中观察到,帮助确定适合的参数。
三、SEM动态水合作用套件SK-202C-24
WETSEM是一个应用于SEM样品台的含水样品室。在样品室的中心区域覆盖一层纳米薄膜,完全将含水样品与电镜真空室隔离,电子束穿透薄膜成像。
SK-202C-24套件包括QX-202C样品室及所有必需配件。
1. QX-202C Capsules (24 units)
2. MP-12 Multi-well Plates (2 units)
3. IB-64 Imaging Buffer
4. Calibration Capsule
5. Applicator (Microman M25 and tips)
6. User Manual, Training CD, Imaging Quick Guide
QX-202C 样品室

QX-202C主要用于不同动态水合过程电镜原位图像制作,例如水泥,石膏等材料的水合过程。QX-202C独特的设计可以应用于SEM真空室。动态过程最长可达24小时,不再需要多个样品成像或反复抽真空。样品不需包埋,干燥及冰冻,可简单放入试剂盒密封观察,可直接用BSE检测器观察。
MP-12 多孔板
多孔板为同时处理多个QX-202C设计,方便多个样品制备时的处理和保存。

QX Imaging Buffer
QX-Imaging buffer适用于SEM成像的标准样品舱。冰冻储存。
标准样品

标准样品帮助第一次使用WETSEM的用户找到扫描电镜成像时的合适参数。标准样品包含40nm和500nm两种不同大小的纳米粒子。纳米粒子很容易在电镜中观察到,帮助确定适合的成像参数。
微分器 (Microman M25 and tips)

Gilson Microman吸管专门为精确移取少量粘稠液体和混合液而设计。同时提供Microman M25连接活塞和枪头。

三、SEM含水固体样品套件SK-302-12
WETSEM是一个应用于SEM样品台的含水样品室。在样品室的中心区域覆盖一层纳米薄膜,完全将含水样品与电镜真空室隔离,电子束穿透薄膜成像。
SK-302-12套件包括QX302样品室及所有必需配件。
1. QX-302 Capsules (12 units)
2. MP-12 Capsule Plates (2 units)
3. IB-74 Imaging Buffer
4. RT-58 Calibration Capsule
5. User Manual, Graphic User Guide, WETSEMTM Imaging Quick Guide
QX-302样品室

QX-302样品室适用于多种含水固体样品,例如活体组织切片,自然状态的植物材料等。样品舱可用于多种样品大小,最大直径为3mm,最大厚度为1mm。扫描样品不需包埋和嵌入。相对于光学电镜,电子显微镜的样品处理更加简单。
MP-12 多孔板

MP-12 多孔板用于同时处理多个QX-302样品室,方便样品制备及储存。
IB-74 Imaging Buffer
QX-Imaging buffer适用于样品室在SEM扫描前处理样品,能降低电子束对样品的损伤。经无菌处理,冷冻保存。
RT-58-标准样品
 标准样品帮助第一次使用WETSEM的用户找到扫描电镜成像时的合适参数。标准样品包含40nm和500nm两种不同大小的纳米粒子。纳米粒子很容易在电镜中观察到,帮助确定适合的成像参数。
标准样品帮助第一次使用WETSEM的用户找到扫描电镜成像时的合适参数。标准样品包含40nm和500nm两种不同大小的纳米粒子。纳米粒子很容易在电镜中观察到,帮助确定适合的成像参数。
The SK-102-302 Starter Kit 包括 QX-102 Capsules and QX-302 Capsules, 及所有必需配件。
1. QX-102 Capsules (12 units)
2. QX-302 Capsules (6 units)
3. MP-10 Multi-well Plates (2 units)
4. MP-12 Capsule Plates (2 units)
5. MA-4 Multi-well Aspirator
6. IB-64 Imaging Buffer
7. IB-74 Imaging Buffer
8. RT-56 Calibration Capsule
9. User Manuals, Applications Manual, Instructional Training Movie, Graphic User Guide, WETSEMTM Imaging Quick Guide

WETSEMTM Technology
§ High resolution imaging of fully hydrated samples
§ Greatly reduces prep time as well as artifacts
§ Capsule and base fits standard SEMs
§ Safe and simple to use
§ Achieve reliable, reproducible, quantifiable results
Electron microscopy (EM) is today's primary tool for high-resolution imaging the cornerstone for research into living organisms and our material environment.
But because EM requires that samples be placed in a vacuum, it has not been suitable for examining wet samples. This single drawback has been a major impediment to the use of EM for biomedical research, as well as for many other clinical and industrial applications. Until now, the only means of imaging a wet sample with EM was to freeze or dry it, effectively changing it's nature in the process. Such sample preparation is also time-consuming, costly, and often introduces artifacts.
El-Mul (QuantomiX) WETSEM developed with the cooperation of some of the world's leading life sciences and materials science researchers and labs dramatically reduces the preparation needs for high-resolution imaging of wet samples, making imaging easier and faster. It also eliminates many of the artifacts that result when preparing wet samples for EM, opening up opportunities for new research methods as well as new processing methodologies in a variety of fields.
WETSEM also uniquely enables imaging of samples that contain oily and volatile materials.
Also for the first time, WETSEM enables microanalysis using energy dispersive spectrometry (EDS) of wet samples in their native state, a long-awaited capability for many industrial and research labs.
Concept
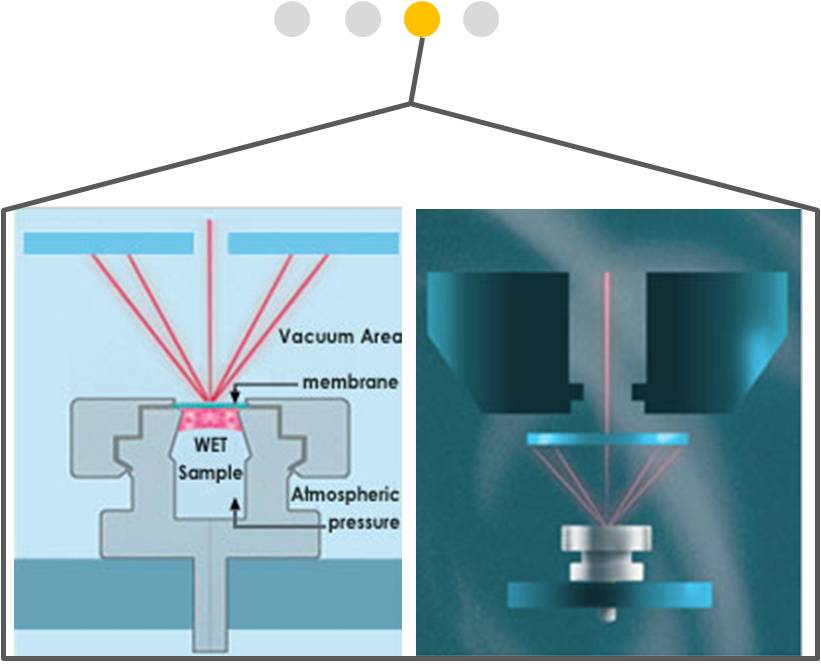
WETSEM Technology is based on a proprietary capsule that is placed on the specimen stage of a standard SEM. At the heart of the capsule is a patented, nanotech-engineered transparent membrane that completely isolates a wet sample from the powerful vacuum used in SEM chambers.
The capsule serves the combined function of specimen holder or cell culture dish, depending on the application. This unique receptacle permits electrons to enter and exit the capsule, while maintaining the sample in its natural state at atmospheric pressure.
Imaging is achieved either with backscattered (BSE) electron detection or X-ray detection, revealing high-resolution structure as well as material composition.
WETSEM is ideally suited for fully-hydrated or liquid-containing samples including foods, oils, cosmetics, ink, biological cells, tissues, and fluid suspensions. In certain settings, WETSEM also enables imaging of dynamic reactions and their products.
Advantages
§ Direct imaging of wet samples (food, cosmetics, inks, cells, tissues)
§ Compositional analysis of wet samples by X-ray microanalysis
§ Wide spectrum of staining and labeling capabilities for cells and tissues
§ Ability to image unstained or unfixed cells and tissues
§ Imaging of both adherent and non-adherent cells
§ High resolution histopathology
§ Intracellular imaging in a scanning EM
§ Imaging the entire cell surface
§ Excellent preservation and imaging of lipid structures
§ Easy-to-automate sample processing and imaging
Capabilities
§ Analyze size distribution, aggregation and homogeneity of particle suspensions.
§ Perform EDS of fully hydrated samples.
§ SEM imaging of oils, greases, volatile substances, emulsions and creams.
§ Enables tissue morphology and analysis.
§ Characterize cellular and subcellular organelles, cell contacts and receptors, cytoskeleton and other detail.
§ Characterize and quantify lipids in fully-wet cells and tissues.
Applications
§ Industrial research: food, oils, dyes, emulsions, pharmaceuticals, suspensions, personal care goods, cosmetics, inks
§ Quality control and quality assurance
§ Life sciences and medicine: cultured and primary cells, histology,nerve cells and myelin imaging, microbiology, plants
§ Tissue implants and prostheses
§ Environmental and toxicological applications
§ Clinical diagnosis: histopathology, cytology, oncology
Recent Publications | |
A. Katz, A. Bentur, and K. Kovlera "A novel system for in-situ observations of early hydration reactions in wet conditions in conventional SEM." Cement and Concrete Research, Volume 37, Issue 1 , January 2007, Pages 32-37. Rossana C. N. Melo, Alon Sabban and Peter F. Weller "Leukocyte lipid bodies: inflammation-related organelles are rapidly detected by wet scanning electron microscopy." Journal of Lipid Research, Vol. 47, 2589-2594, November 2006. Ohad Cohen, et al. "Scanning Electron Microscopy of Thyroid Cells Under Fully Hydrated Conditions - A Novel Technique for a Seasoned Procedure: A Brief Observation." Thyroid Oct 2006. Volume 16, Number 10, 2006: 997-1001. Stephan Thiberge et al. "Scanning electron microscopy of cells and tissues under fully hydrated conditions." PNAS, March 9, 2004. Applied Physical Sciences, Applied Biological Sciences, Volume 101 no. 10. Winston Timp, et al. "Wet electron microscopy with quantum dots." Irit Ruach Nir "A Capsule for Dynamic In-Situ Studies of Hydration Processes by Conventional SEM." Microscopy & Analysis, July 2006. David C. Joy "Scanning electron microscope imaging in liquids - some data on electron interaction in water." Journal of Microscopy, Vol.221, Pt 2 February 2006, pp. 84-88. Federica Boraldi, et al. "Identification of Mineralized Elastic Fibers on Wet Samples by SEM"MICROSCOPY RESEARCH AND TECHNIQUE Volume 67, Issue 6, 2005. Pages 296-299. Guo W, et al. "A new scanning electron microscope method for determination of adipocyte size in human fat tissue: Correlation with weight loss and fat depot burden"poster presentation at the annual meeting of NAASO, the Obesity Society, Vancouver 2005. Abraham Nyska et al. "A new method of wet scanning electron microscopy for the analysis of myelination in EAE mouse model of multiple sclerosis" EXPERIMENTAL AND TOXICOLOGIC PATHOLOGY, November 2005. Irit Ruach-Nir "An Innovative Method for Imaging and Chemical Analysis of Wet Samples in Scanning Electron Microscopes" MICROSCOPY TODAY, July 2005. Vered Behar "Applications of a Novel SEM Technique for the Analysis of Hydrated Samples"Microscopy & Analysis, Issue 108, July 2005. Iris Barshak et al. "Wet SEM: A Novel Method for Rapid Diagnosis of Brain Tumors" Ultrastructural Pathology, 28:255-260, 2004. Stephan Thiberge et al. "An apparatus for imaging liquids, cells and other wet samples in the scanning electron microscope." Review of Scientific Instruments, Volume 75 no. 7, July 2004. Abraham Nyska et al. "Electron Microscopy of Wet Tissues: A Case Study in Renal Pathology."Toxicologic Pathology, Volume 32 no. 3, May 2004. Iris Barshak et al. "A Novel Method for 'Wet' SEM." Ultrastructural Pathology, Volume 28, Number 1 / January-February 04. Opher Gileadi et al. "Squid Sperm to Clam Eggs: Imaging Wet Samples in a Scanning Electron Microscope." Biol. Bull. 205: 177�179. October 2003, Marine Biological Laboratory. |


